Encyclopedia
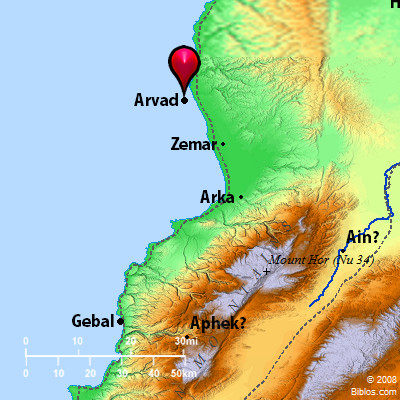
ARVAD; ARVADITESar'-vad, ar'-vad-its ('arwadh; Arados; modern Ruad): An island city off the coast of Syria some 30 miles North of Tripolis, and the race inhabiting it. It was a barren rock covered with fortifications and houses several stories in height. The island was about 800 ft. long by 500 wide, surrounded by a massive wall, and an artificial harbor was constructed on the East toward the main land. It developed into a trading city in early times, as did most of the Phoenician cities on this coast. It had a powerful navy, and its ships are mentioned in the monuments of Egypt and Assyria. It seems to have had a sort of hegemony over the northern Phoenician cities, from Mt. Cassius to the northern limits of Lebanon, something like that of Sidon in the South. It had its own local dynasty and coinage, and some of the names of its kings have been recovered. Its inhabitants are mentioned in the early lists of Genesis 10:18, and Ezekiel 27:8, 11 refers to its seamen and soldiers in the service of Tyre. It brought under its authority some of the neighboring cities on the main land, such as Marathus and Simyra, the former nearly opposite the island and the latter some miles to the South.
Thothmes III, of Egypt, took it in his campaign in north Syria (1472 B.C.) and it is noticed in the campaigns of Rameses II in the early part of the 13th century B.C. (Breasted, Ancient Records). It is also mentioned in the Tell el-Amarna Lettersas being in league with the Amorites in their attacks upon the Egyptian possessions in Syria (44 and 28, B.M. Tell el-Amarna Letters). About the year 1200, or later, it was sacked by invaders from Asia Minor or the islands, as were most of the cities on the coast (Paton, Syria and Palestine, 145) but it recovered when they were driven back. Its maritime importance is indicated by the inscriptions of the Assyrian kings. Tiglath-pileser I (circa 1020) boasts that he sailed in the ships of Arvad. Asshur-nazir-pal (circa 876) made it tributary, but it revolted and we find 200 men of Arvad mentioned among the allies of Benhadad, of Damascus, at the great battle of Quarqar, when all Syria seems to have been in league against Shalmaneser II (circa 854). At this time the king of Arvad was Mattan Baal.
It was afterward tributary to Tiglath-pileser III and Sennacherib, the king who paid it to the latter being Abd-ilihit (circa 701). Ashurbanipal (circa 664) compelled its king Yakinlu to submit and send one of his daughters to become a member of the royal harem (Rawlinson, Phoenicia, 456-57). Under the Persians Arvad was allowed to unite in a confederation with Sidon and Tyre, with a common council at Tripolis(ib 484). When Alexander the Great invaded Syria in 332 B.C. Arvad submitted without a struggle under her king Strato, who sent his navy to aid Alexander in the reduction of Tyre. It seems to have received the favor of the Seleucid kings of Syria and enjoyed the right of asylum for political refugees. It is mentioned in a rescript from Rome about 138 B.C., in connection with other cities and rulers of the East, to show favor to the Jews. It was after Rome had begun to interfere in the affairs of Judea and Syria, and indicates that Arvad was of considerable importance at that time (see 1 Maccabees 15:16-23). The town is not mentioned in the New Testament, and in modern times has sunk to a small village, chiefly inhabited by fishermen. See ARADUS.
H. Porter